Survey of Youth and Young Adults on Vocations: Major Findings
Consideration of Priesthood and Religious Life Among Never-Married U.S. Catholics by the Center for Applied Research in the Apostolate at Georgetown University - Washington, D.C.
Major Findings
This study identifies subgroups in the never-married Catholic population—including teens and adults—and compares those who have considered a vocation at least “a little seriously” to those who say they have not considered this or who say they did so, but not seriously.
Overall, 12 percent of male respondents say they considered becoming a priest or brother at least a little seriously. Ten percent of female respondents say they considered becoming a religious sister at least a little seriously. The subgroups that are especially likely to have considered a vocation include:1
- Weekly Mass attenders (now and in high school)
- Those who attended Catholic educational institutions at any level (excluding parish-based religious education)
- Those who participated in Church-related groups, programs, or activities as a youth or young adult
- Those who lived in households where parents talked to them about religion at least once a week
- Those who say their faith is the most important part of their life (now and in high school)
- Those who participate in prayer and devotional activities, groups, or programs (e.g., Bible study, Eucharistic adoration, retreats, or prayer groups)
- Those who pray the rosary at least weekly (alone or in a group)
- Those belonging to a group that encourages devotion to Mary
- Those who were encouraged to consider a vocation by someone else (e.g., family, friends, clergy, religious)
- Those who regularly read the Bible or pray with Scripture
- Those who personally know priests and men and women religious (in their extended family or outside of it)
- Those who have participated in parish ministry (e.g., Lectors, Ministers of Holy Communion, Youth Ministers)
- Those who have participated in World Youth Day or a National Catholic Youth Conference
- Those who have recently accessed religious and spiritual content in traditional or new media
Individual Characteristics
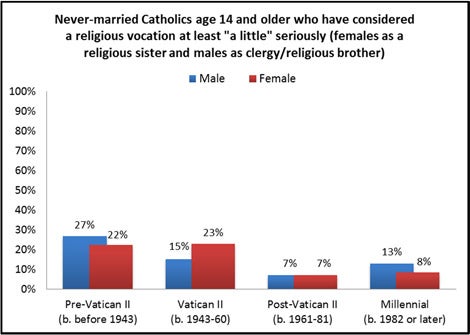
There are generational differences in the consideration of vocations. A low point appears within the Post-Vatican II Generation (i.e., those born 1961 to 1981) with less than one in ten male and female respondents of this generation saying they have considered a vocation at least “a little” seriously. Vocational consideration appears to rebound slightly among the Millennial Generation (i.e., those born after 1981), particularly among men of this generation.
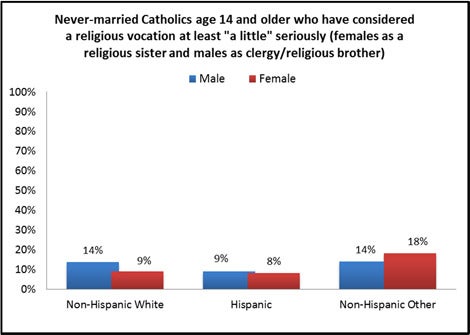
There are few differences related to race and ethnicity. Hispanic respondents—both male and female—are no less likely than others to say they have considered a vocation. Although there is a slight numeric difference, this is not statistically significant (i.e., within sub-group margins of sampling error). However, as shown in the figure on the next page, female respondents who self-identify as other than white or Hispanic are significantly more likely than others to say they have considered becoming a religious sister.2
Beliefs and Practices
Outside of generation and race and ethnicity, many of the subgroups differences identified in the study are related to participation in groups, activities, and personal relationships. Surprisingly, there are fewer subgroup differences related to matters of belief. For example, those who believe in the Real Presence are no more likely to have considered a vocation than those who do not (accounting for subgroup margins of error and statistical significance). One’s conception of God (including beliefs about having a personal relationship with God) is also unrelated to the consideration of vocations.
Combined Influences
The results above are based on rather simple comparisons—whether one does something or does not or whether one has or has not been encouraged. The study also weighed the relative importance of each of these factors as being potentially influential to vocational consideration simultaneously—controlling for the effects of all other factors to discern what is most important and to weed out influences that are related to a common cause. Within these models—which are gender specific—we include substantive variables (e.g., Mass attendance, enrollment in Catholic schools) and control variables that measure race and ethnicity as well as age. These models utilize logistic regression—a statistical method for predicting which of two categories a person is likely to be in given other information we know about them. For this study, these two groups are: A) those that have considered a vocation at least a little seriously or more and B) those who have not considered this or those who have, but not seriously at all. The logistic regression models predict the probability of respondents considering a vocation given their responses to other questions in the survey.
In two baseline models—one for men and the other for women—neither ethnicity nor age is shown to be a strong predictor. Thus, controlling for both factors, neither the participant’s age nor their being Hispanic or not make them more or less likely to consider a vocation. However, among women, being of a race and ethnicity other than non-Hispanic white or Hispanic does make one more than twice as likely to consider a vocation compared to those who are non-Hispanic white or Hispanic.3 Among men, Millennial teens (those ages 14 to 17) are less likely than never-married Catholics of the oldest generation (those born before 1943) to say they have considered becoming a priest or religious brother. A comprehensive model—including 39 different variables—increases the amount of variation explained by a factor of 7 for both male and female respondents.
Consideration of Becoming a Priest or Religious Brother among Men
Among male respondents, after controlling for all other factors, those who attended a Catholic secondary school (grades 9-12) are more likely to have considered becoming a priest or religious brother. Compared to those who did not attend a Catholic secondary school, these respondents are more than six times as likely to have considered a vocation. Participation in a parish youth group during primary school years (grades K-8) is also strongly related to vocational consideration. These respondents are more than five times as likely to consider a becoming a priest or religious brother than those who did not participate in a parish youth group. Given that 75 percent of male respondents who have considered a vocation report that they first did so when they were 18 or younger, these two results provide some of the strongest evidence of a possible causal effect.
Encouragement from others is also important. Respondents who have one person encouraging them are nearly twice as likely to consider a vocation as those who are not encouraged. Each additional person encouraging these respondents increases the likelihood of consideration. The effect is additive. Respondents who had three persons encourage them would be expected to be more than five times more likely to consider a vocation than someone who was not encouraged by anyone.
Knowing someone who has become a priest, religious sister or brother, or seminarian also has a positive effect. Respondents who personally know one of these individuals are more than one and a half times more likely than someone who does not to consider a vocation themselves. This effect is also additive and knowing more of these individuals would be expected to increase the likelihood of a respondent considering a vocation.
Attendance at World Youth Day or at a National Catholic Youth Conference has a positive effect for male consideration of a vocation. Those who attended either of these events are more than four times as likely as those who have not to say they have considered becoming a priest or brother.
Finally, those who have recently used traditional media (television, radio, print) to access content about religion or spirituality in the 12 months prior to the survey are more likely than those who did not to say they have considered a vocation. Note however, that this media use in most cases occurred well after their initial consideration. Thus, what this more likely demonstrates is that people who have considered a vocation are more likely than those who have not to use traditional media to currently follow religion and spirituality content. Those who have used one type of traditional media in the last year are nearly twice as likely to say they have considered a vocation than those who have not used these media recently. The effect is additive, so use of two or three traditional media to access religious or spiritual content is associated with an even greater likelihood of vocational consideration. This finding is potentially useful in understanding how male never-married Catholics who have considered becoming a priest or religious brother can be reached now.
Note that neither generation nor race and ethnicity are statistically significant in the full model. Thus, there is nothing about a person’s age or race and ethnicity that are associated with lower or higher likelihoods of consideration, controlling for all other factors. Any disproportionality in the race and ethnicity of men who decide to become priests or religious brothers are in part likely to be related to being less likely to attend Catholic schools or to be involved in youth groups, comparatively lower levels of encouragement, or not personally knowing clergy or religious. This could also be related to factors that are important after consideration of a vocation is made by individuals, such as meeting requirements for entry into a formation program.
Consideration of Becoming a Religious Sister among Women
Among female respondents, the model predicting consideration of becoming a religious sister includes many parallel results to the model for male respondents.
Whereas secondary school is important for male vocational consideration, it is attendance at a Catholic primary school which is important for female vocational consideration. Female respondents who attended a Catholic primary school are more than three times as likely as those who did not to consider becoming a religious sister. Parish youth group participation is also important for female respondents. However, unlike males, it is participation during high school years rather than primary school years that has an effect. Women who participated in a parish youth group during these teen years are more than nine times as likely to consider becoming a religious sister.
Similar to male respondents, encouragement is also a positive factor. With nearly the same effect as is demonstrated among men, women are nearly twice as likely to consider a vocation when encouraged by another person to do so.
Also parallel to men, women who have used traditional media in the last year to consume or follow religious or spiritual content are more likely than those who do not to say they have considered a vocation.
Among the adults surveyed (excluding those ages 14 to 17 in the sample) who say they have considered a vocation, most report that they did so between the ages of 13 and 24. Additionally, one in four Catholic females who have considered becoming a religious sister did so before they were a teenager.
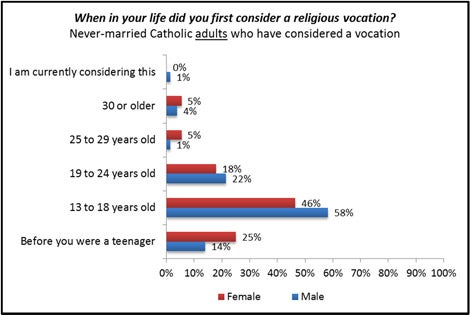
Although most Catholics who are becoming priests, religious brothers, or religious sisters now are typically in their 30s or even older, it is likely that the roots of these vocations were established in their teen years or even earlier.
In Their Own Words
Respondents who said they had never considered a vocation were asked in an open ended question, “Why do you think you have never considered this?” Their responses to this question were coded into categories based on their content.
Among male respondents who have never considered a vocation as a priest or religious brother, the most common responses to the question were related to a general lack of interest (39 percent), celibacy (18 percent), not having a calling to seek a vocation (8 percent), having other life goals (8 percent), and having some doubts about their faith or not feeling religious enough to seek a vocation (8 percent). One percent of comments referenced the issue of sexual abuse of minors by clergy.
Among female respondents who have never considered a vocation as a religious sister, the most common responses were related to a general lack of interest (31 percent), celibacy (16 percent), not having a calling to seek a vocation (11 percent), discomfort with the lifestyle they would need to adopt (10 percent), and having some doubts about their faith or not feeling religious enough to seek a vocation (9 percent).
Challenges
To the degree that vocational formation programs have educational prerequisites including college, Hispanic adult Catholics who have considered a vocation may face additional challenges, as Hispanic respondents are the least likely to report attending college or obtaining a college degree. Hispanic respondents are also the least likely to indicate enrollment in a Catholic school at any level of their education and the results of the study suggest that this makes it less likely that they will consider a vocation.
At the same time, Hispanic respondents are among the most likely to participate in devotional practices and other prayer that is associated with a greater likelihood of considering a vocation. For example, a majority of Hispanic adults and teens (63 percent and 53 percent, respectively) indicate that they pray the rosary. By comparison, less than four in ten non-Hispanic white adults and teens say they do so (36 percent and 32 percent, respectively).
At the same time, Hispanic respondents are among the least likely to report that they have ever been encouraged to seek a vocation. This may be in part because they are less likely to be enrolled in a Catholic school or registered with a Catholic parish. It is also the case that family members of Hispanic respondents are less likely to encourage vocations. Among Hispanic males who have not considered a vocation seriously, 37 percent agree “somewhat” or “very much” that they have never felt invited by the Catholic Church to consider this. By comparison, only 22 percent of non-Hispanic white male respondents indicate this.
One in five Hispanic respondents (21 percent) also indicates that citizenship requirements prevented their serious consideration of becoming a priest or religious brother. Two-thirds of Hispanic never-married males (66 percent) agree at least “somewhat” that their desire to be a father prevented their serious consideration of a priestly or religious vocation. By comparison only 51 percent of non-Hispanic white male respondents indicated this.
Conclusion
Although many speak of priest shortages and steep declines in the number of men and women religious, the survey reveals that there is no shortage of individuals who seriously consider these vocations among never-married Catholics in the United States.4 Three percent of men say they have “very seriously” considered becoming a priest or religious brother and 2 percent of women indicate they have “very seriously” considered becoming a religious sister. This is equivalent to 350,000 never-married men and more than 250,000 never-married women.5 Shepherding more of these individuals on the path to seeking a vocation would likely require a combination of greater outreach from the Church, encouragement from others, assistance in obtaining educational prerequisites, and dealing with other issues such as student loan debt and citizenship status.
Footnotes
- It is important to clarify here that correlation does not equal causation. For example, someone who participates in Eucharistic Adoration may be more likely to consider a vocation. But is it this participation that led to the consideration? Probably not. Instead there is likely some third factor (e.g., religiosity) that leads the individual to both participate in Eucharistic Adoration and consider a vocation.
- The majority of the women in this “other” race and ethnicity group who have considered becoming a religious sister are Asian.
- This group consists largely of Asian and African American Catholics. The sample sizes for both of these groups as well as those of other races and ethnicities are too small to make reliable comparisons in isolation. These groups must be combined for statistical analyses.
- Relative to the Church’s needs and the number of clergy and vowed religious in recent history.
- Including those who have married, an even larger number of Catholics have very seriously considered a vocation.